Domain And Range Given Points

Column two list the corresponding function values.
Domain and range given points. Square root of cos x. Given the graph of a function determine its domain or range. Given the graph identify the domain and range using interval notation. Can a function s domain and range be the same.
Enter your queries using plain english. For example the domain and range of the cube root function are both the set of all real numbers. The given table has two columns. Given the graph of a function determine its domain or range.
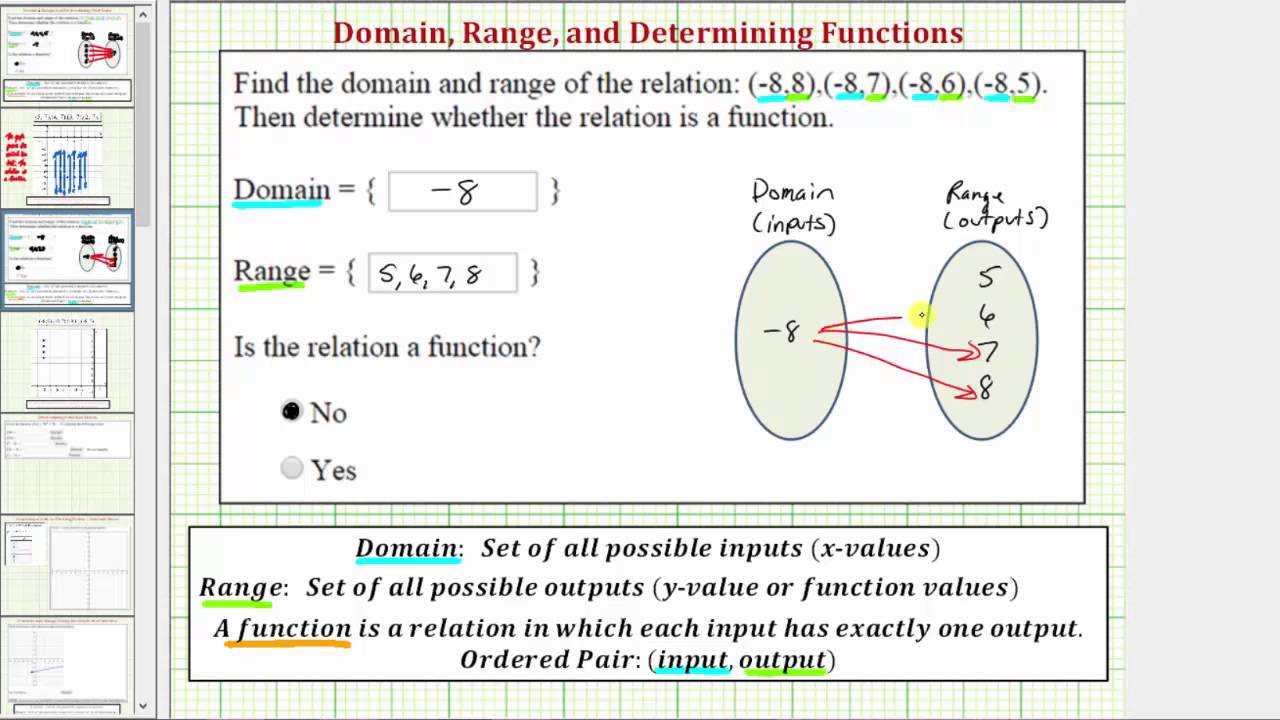
The above list of points being a relationship between certain x s and certain y s is a relation. The arrow at the top right of the graph indicates that the graph continues to the left as x increases. The set of values points which a function can obtain. To find the range of a function first find the x value and y value of the vertex using the formula x b 2a.
When x 3 f x 11 w. The domain is all the x values and the range is all the y values. Find the domain and range of the relation given by its graph shown below and state whether the relation is a function or not. The horizontal and vertical line test can help determine the type of relation between the domain and range.
Values in the domain map onto values in the range. The range of a function is all the possible values of the dependent variable y. To avoid ambiguous queries make sure to use parentheses where necessary. Domain and range of toolkit functions.
The example below shows two different ways that a function can be represented. Find the domain of 1 e 1 x 1 function domain. We will now return to our set of toolkit functions to. To give the domain and the range i just list the values without duplication.
To find the domain of a function just plug the x values into the quadratic formula to get the y output. The domain of a function is the collection of independent variables of x and the range is the collection of dependent variables of y. Here are some examples illustrating how to ask for the domain and range. The domain and range of a function is all the possible values of the independent variable x for which y is defined.
The set of all points over which a function is defined. As a function table and as a set of coordinates. Column one lists the x values. Domain of log x x 2 1 x 2 1 domain.
2 3 4 6 range. Points a 3 0 has the smallest x coordinate.