Domain Generation Algorithm Explained
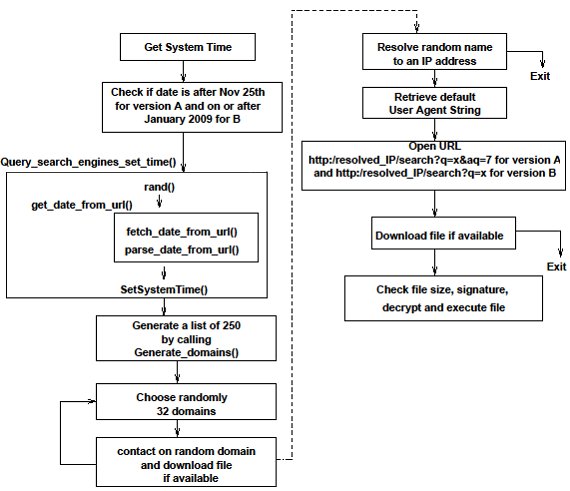
Domain generation algorithm dga.
Domain generation algorithm explained. In order to form a possible domain name. Domain fluxing is a technique used by botnets and command and control c2 servers to create many domains using a domain generation algorithm dga 7 8. The seed is a piece of information accessible to both the bot herder and the infected host now acting as a bot. Both malware instances spread on various devices and the hacker controlled software should be able to run the algorithm and produce the same values at a given time.
Attackers developed dgas so that malware can quickly generate a list of domains that it can use for the sites that give it instructions and receive information from the malware usually referred to as command and control or c2. All dgas are based off of a static and dynamic seed which ensures that the domains are constantly changing. A domain generating algorithm dga is a program or subroutine that provides malware with new domains on demand or on the fly. A domain generation algorithm is a program that is designed to generate domain names in a particular fashion.
A subset of these domains. Part of this is due to how the algorithm is set up and how easy they are to update. Kraken was the first malware family to use a dga in 2008 that we could find. A basic implementation uses 3 specific parts.
Later that year conficker made dga a lot more famous. For a dga to be functional idempotence on domain generation is required. A domain generation algorithm dga is a computer program that creates slightly different variations of a given domain name. Domain generation algorithms dga are algorithms seen in various families of malware that are used to periodically generate a large number of domain names that can be used as rendezvous points with their command and control servers the large number of potential rendezvous points makes it difficult for law enforcement to effectively shut down botnets since infected computers will attempt to.