Domain Group Policy Editor Command Line

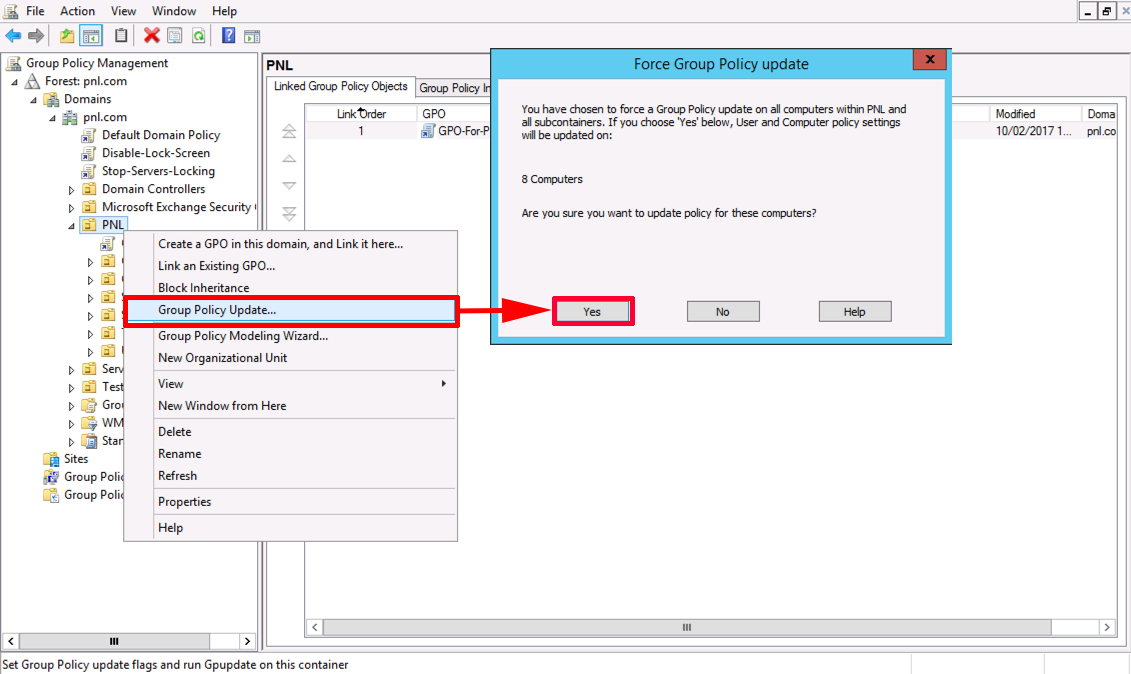
To update refresh and apply the new group policy settings gpresult.
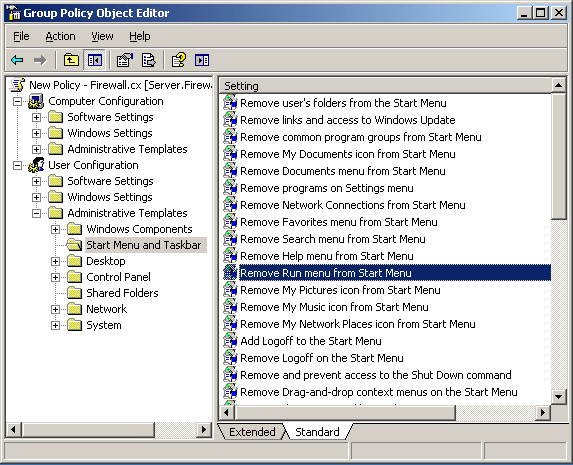
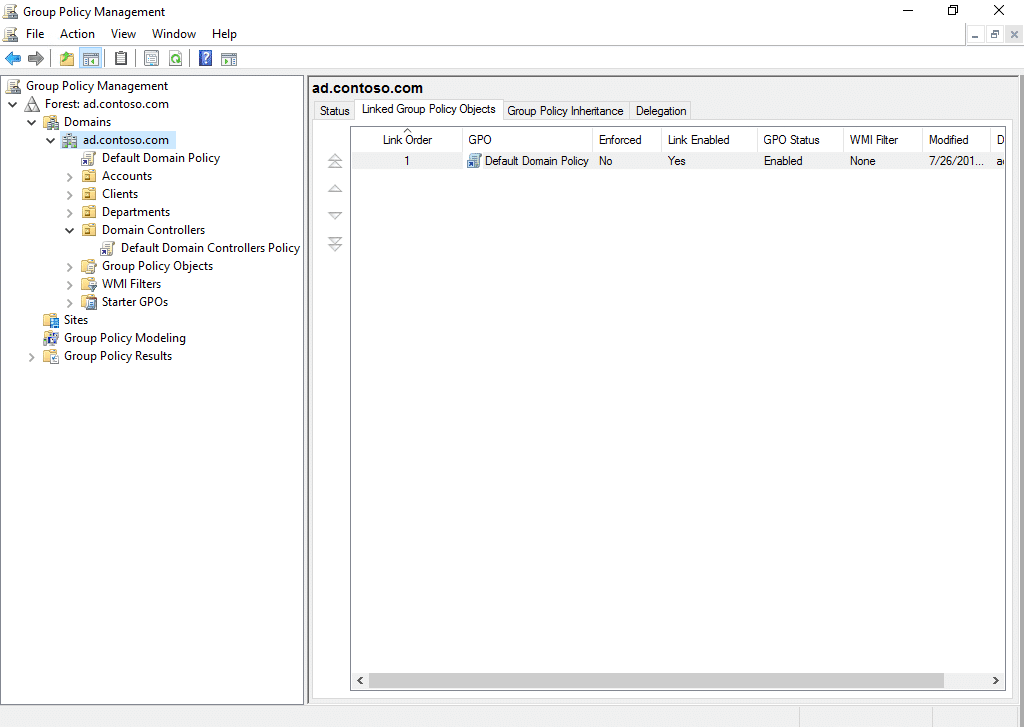
Domain group policy editor command line. In the left side pane you can see a node with the domain name. To change settings for a policy you right click it and choose edit. To access the local group policy gpmc msc. To view the apploied gpos and some settings.
And it provides a simple graphical interface for browsing through the group policy settings currently in effect on. Opening group policy management editor from the command line date tue 19 march 2013 tags group policy programming scripts powershell active directory yesterday i wanted to open the group policy editor or group policy management editor for a specific gp object through powershell but there is no edit gpo cmdlet. 5 ways to access local group policy editor on windows 10. Now it will open a new window on which we need to select the group policy tab.
To open the gpedit msc tool from a run box press windows key r to open up a run box. Now select the appropriate group policy object in the list and then click on edit. For more info please keep on reading. Noe that there ares some other commands can be used on powershell for managing and dministering gp.
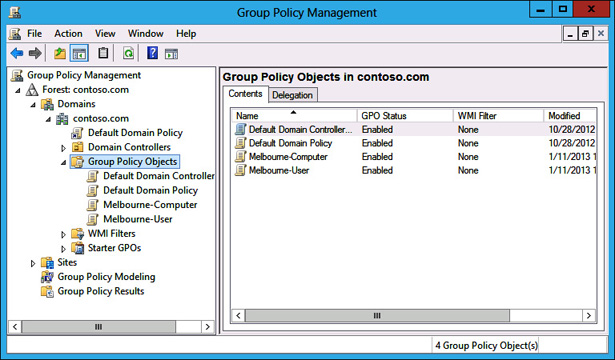
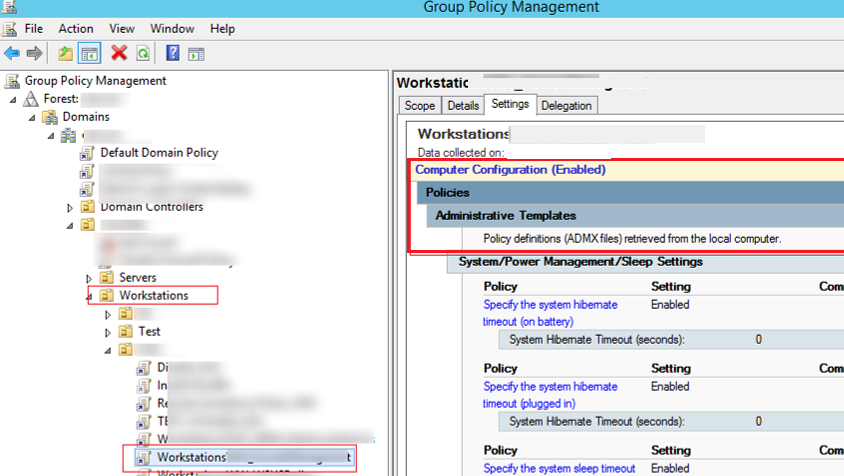
But if you try that on a rsat installed sp1 vista system you will get the default domain policy but you won t see any of the group policy preferences options. You can also see a list of group policy objects and wmi filters at the bottom of each domain which you can backup import restore and save to a report. This is one of the quickest ways to access the local group policy editor. If you usually use local group policy editor i recommend you create local group policy editor shortcut on desktop.
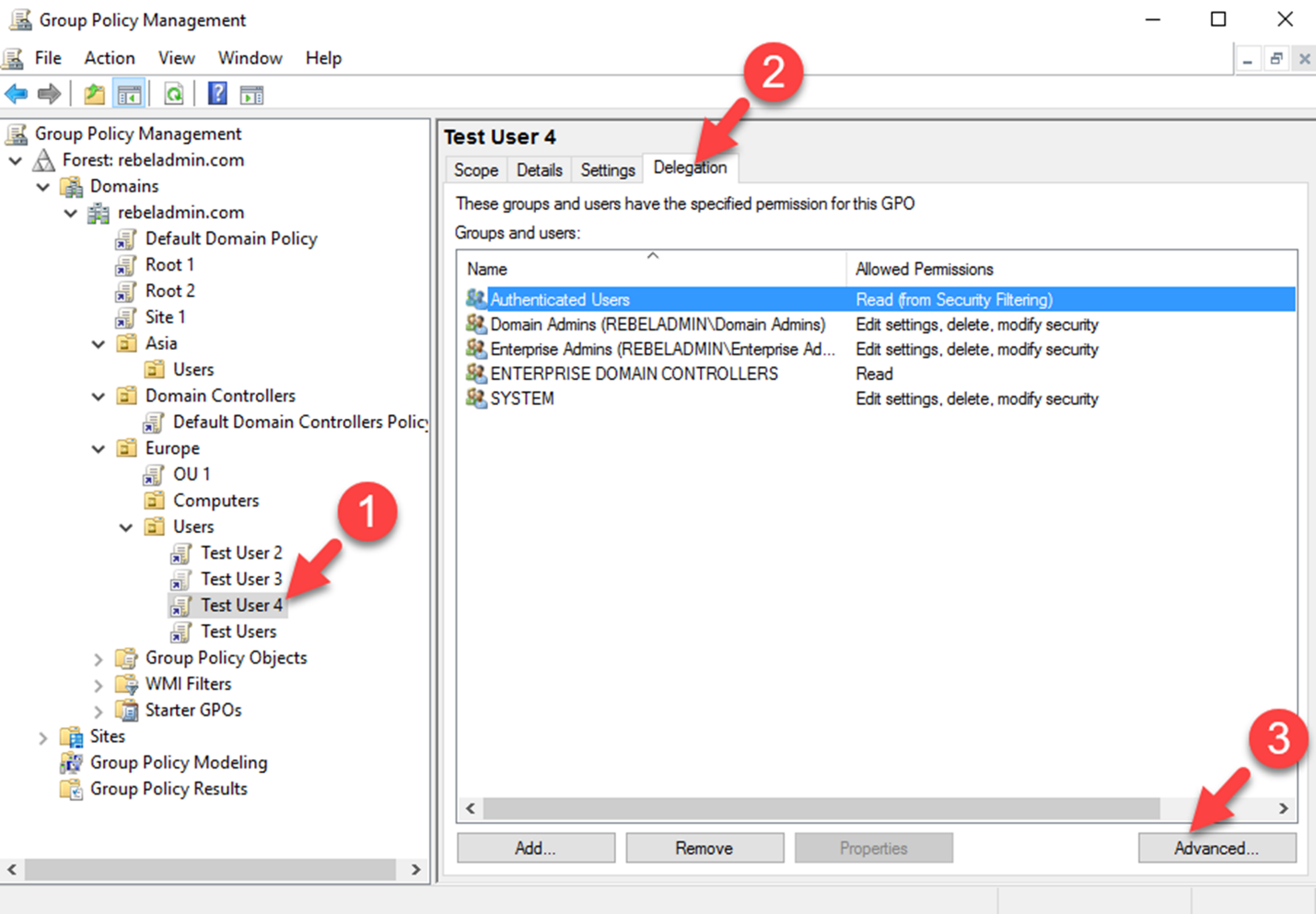
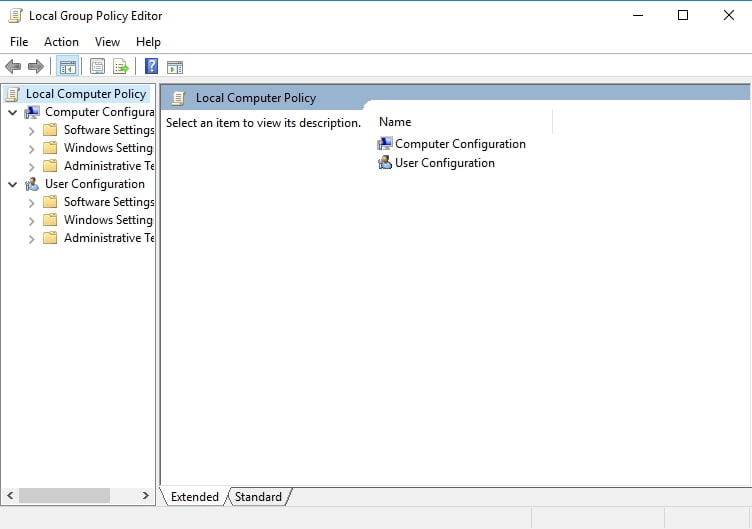
Open local group policy editor via a run box. You will then get the familiar group policy editor. Now this will open group policy object editor. Right click on it and then click on properties.
You can access the local group policy editor see the following picture on your windows 10 computer with the help of run search start menu command prompt and windows powershell. Then type gpedit msc and hit enter to open the local group policy editor. However it does show pretty much all the policies you will have set for regular use.