Z Domain Transfer Function

As we have seen in z transforms the convolution in the time domain transforms to a multiplication in the z domain.
Z domain transfer function. Zplane the function zplane creates a plot of the positions of zeros and poles in the plane of the complex variable z with the unit circle for reference starting from the coefficients a and b. Using this table for z transforms with discrete indices. Likewise in the z domain the transfer function fully describes how the output signal y z responds to an arbitrary input signal x z. The transfer function h z is represented by means of the vectors a and b in several matlab functions as described in the following.
Prototype second order system ζ 1 underdampded prototype 2 nd order lowpass step. For instance consider a continuous time siso dynamic system represented by the transfer function sys s n s d s where s jw and n s and d s are called the numerator and denominator polynomials respectively. Z domain generic decaying oscillatory. For example consider an integrator as a function of time.
This is easily accommodated by the table. F g n γ n z f z g z. After normalizing the denominator of the resulting z domain transfer function we rearrange it to solve for the output. The transfer function in the z domain.
The process of transforming a continuous time transfer function to digital control code is as follows. While this mapping is necessarily nonlinear it is useful in that it maps the entire. So it can be said for a system that produced an output v 0 which was equal to the integral of the input v 1 that. Frequency domain transfer functions describe the relationship between two signals as a function of s.
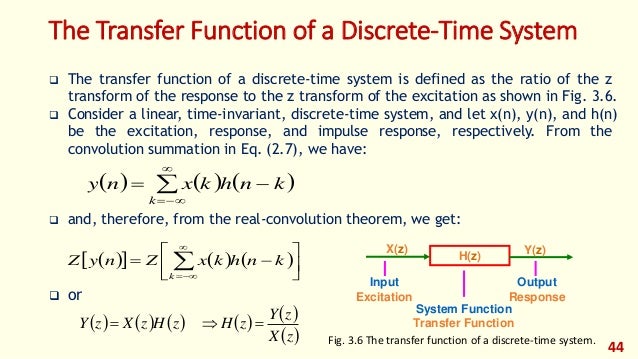
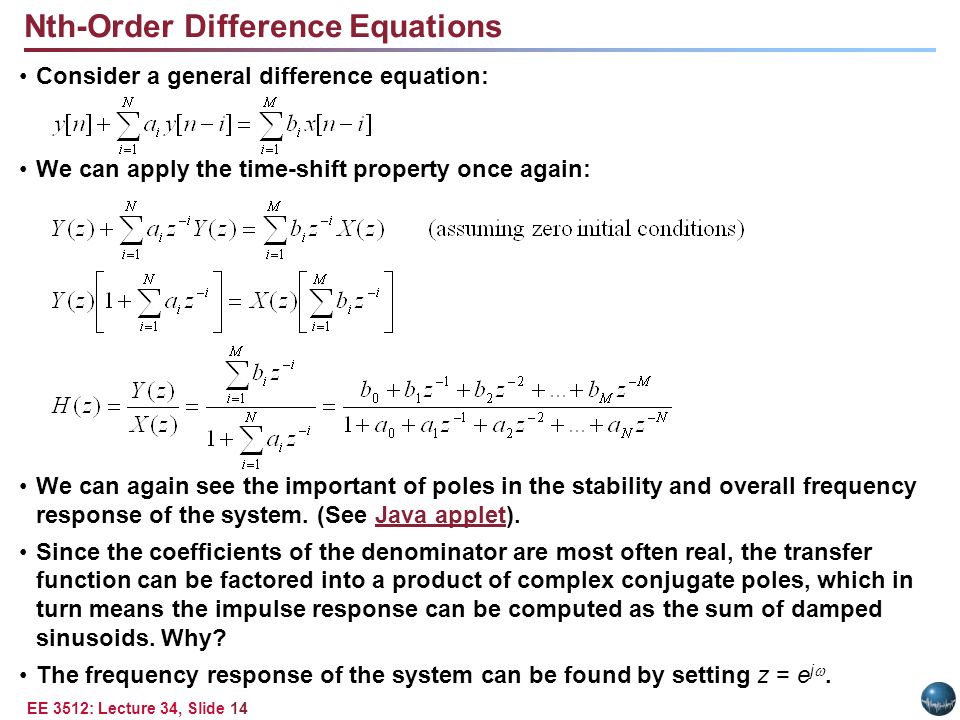
The transfer function in the z domain newcommand op 1 mathsf 1 newcommand ztarrow stackrel op z longrightarrow a lti system is completely characterized by its impulse response h n or equivalently the z transform of the impulse response h z which is called the transfer function. Commonly the time domain function is given in terms of a discrete index k rather than time. For example if you are given a function. From table 3 1 the integrator has an s domain transfer function of 1 s.
Transfer functions are a frequency domain representation of linear time invariant systems. The transfer function of an lti is as shown before without specifying the roc this could be the z transform of one of the two possible time signals. The tf model object can represent siso or mimo transfer functions in continuous time or. If i.
We use the bilinear transformation to map the transfer function from the complex s plane to the complex z plane. To convert some function in the laplace domain to a function in the z domain tustin transformation or from the z domain to the laplace domain. Since t kt simply.