How Is The Domain Eukarya Further Divided Into Kingdoms
The broadest group is the domain.
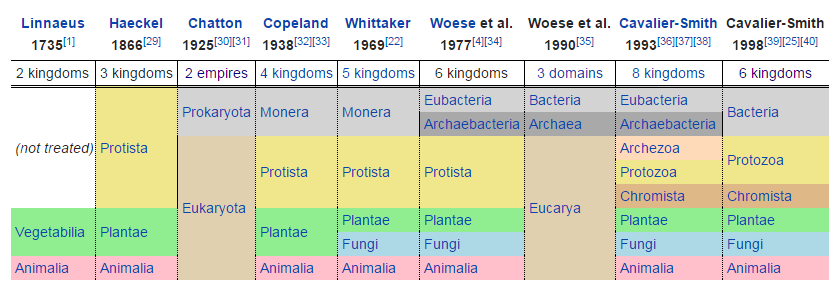
How is the domain eukarya further divided into kingdoms. Plant and fungi organisms contain cell walls that are different in composition than bacteria. This kingdom divided into 3 main groups or phyla. The kingdom animalia is one of four kingdoms in the domain eukarya. Get an answer for of the three domains organisms are further divided into six kingdoms.
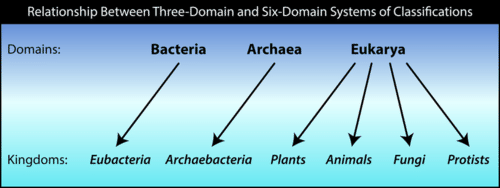
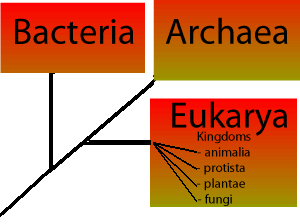
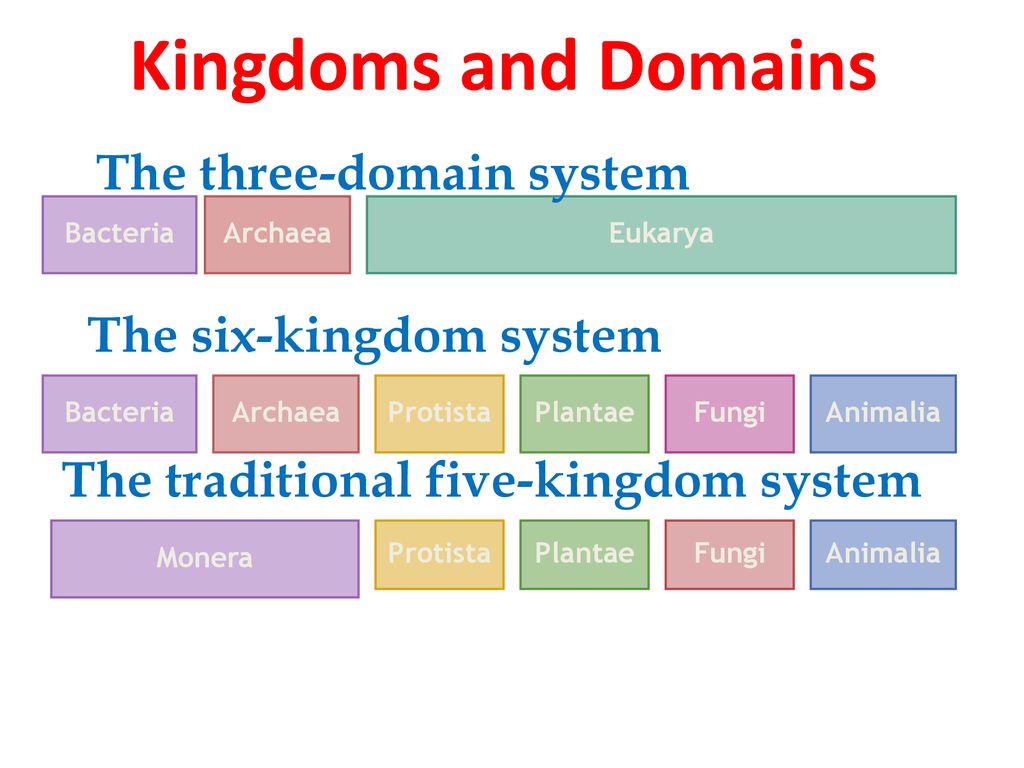
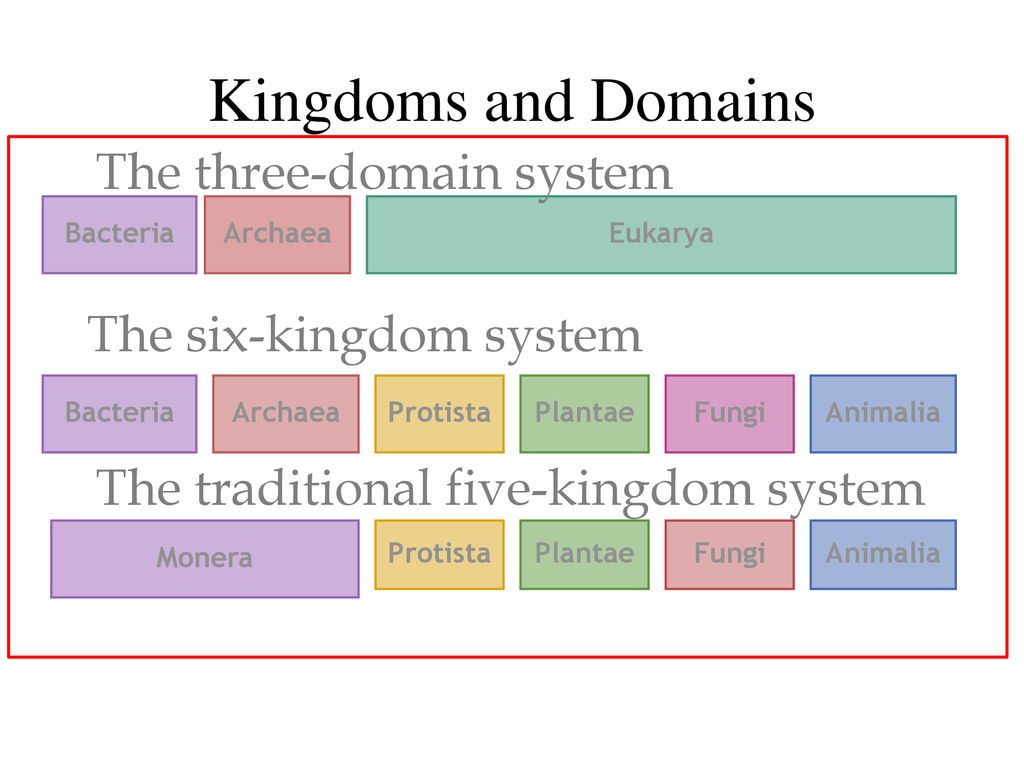
Protists are eukaryotes and contain organelles and a true nucleus. This domain is further subdivided into the kingdoms protista plantae fungi and animalia. 6 eubacteria archaebacteria protista plantae fungi animalia. During mitosis the nucleus of the cell divides into two while the genetic material present as chromosomes are equally distributed to each opposite of the cell.
Archaea are divided into three main phyla. Eukaryotes have rrna that is distinct from bacteria and archaeans. Some truly multicellular algae. Protozoa algae except for.
Most unicellular but some form colonies. Each domain is subdivided into kingdoms followed by phyla class order family genus and species. Many biologists recognize these six kingdoms and three domains but some biologists use other systems of grouping. The six kingdoms consist of four kingdoms within the domain eukarya the kingdoms animalia plantae fungi and protista one kingdom in the domain archaea kingdom archaea and one kingdom in the domain bacteria kingdombacteria.
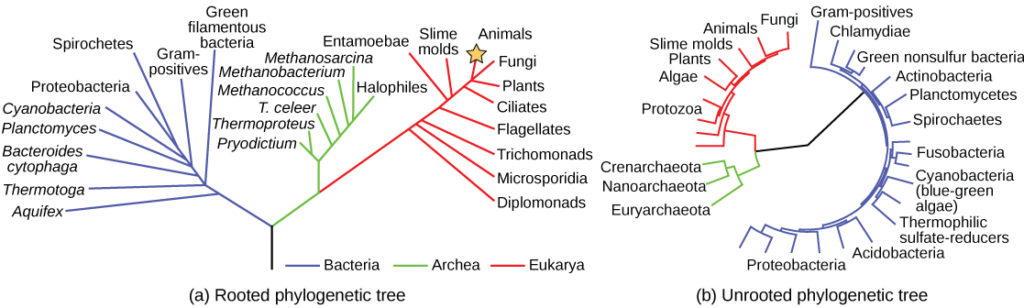
This includes within hydrothermal vents acidic springs and under arctic ice. These organisms are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Scientists use a branching system of classifi cation. There are a total of kingdoms.
Compare and contrast the characteristics of. This domain is further subdivided into the kingdoms protista. We will focus on domains and kingdoms. Further divided into four large groups kingdoms.
Instead of merely dividing themselves and copying their genetic materials like what other domains do cell division in eukaryotes involves two processes. Organisms within kingdoms are given scientific names the naming of living organisms has revealed the biodiversity of the earth eukarya is divided into four kingdoms. There are main kingdoms in domain eukarya. Eukaryota consists of organisms that have a true nucleus and structures called organelles that are surrounded by membranes.
Kattyahto8 and 3 more users found this answer helpful 5 0. Protists plants producers photosynthesis fungi animals consumers consume organic material of other forms of life.